Summary: As learning platforms shift focus from hosting and tracking simple training programs to supporting more complex learning situations for individual employees, the demand for smart virtual tours, immersive scenarios, and simulations will grow.
Why Immersive Simulations Are The Next Big Thing
Several branches of learning and development research have shown that individuals learn more efficiently from on-the-job experiences and less efficiently from courses and reading. As workplaces, offices, training centers, and campuses remain closed, organizations are adopting immersive technologies for distance training, meetings, and even to provide customer service. According to ILO [1], 35% of technical and vocational schools are planning to invest in virtual reality already in 2021.
Up until now, virtual tours, training environments, and simulations have not been part of the standard experience of an LMS, LXP [2], or an online course platform. This is partially due to the high cost related to the development of virtual training and simulations, as well as due to the lack of interoperability between different software. Even large companies are hesitant to invest in expensive VR headsets due to the lack of virtual training content and the high cost associated with creating simulations that will quickly become obsolete.
Image-Based Simulations
The evolution of image capture and media annotation technologies has opened up new possibilities for creating VR/AR learning environments and immersive simulations utilizing consumer devices. In this case, high-quality 2D, 3D, and 360 media from local environments work as the basic building blocks of virtual tours, simulations, and branched scenarios. The visual media elements can first be enriched with useful information, audio narration, notes, and links, and then combined into immersive scenarios or simulations. Whereas previously, these simulations were only accessible on the platform they were created; existing standards such as LTI 1.3 make it now possible to embed various types of interactive scenarios and simulations in any LMS, similar to other media.
3 Reasons Learning Platforms Will Support VR And Immersive Learning Experiences
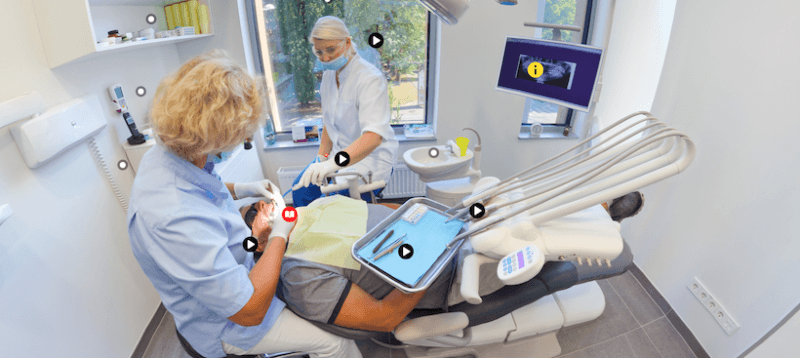
Here are 3 main reasons why we believe most learning platforms will start supporting virtual reality and other immersive learning experiences on their platform:
1. Immersive, Virtual Experiences Are The Fastest Way To Upskill Employees
Experiential learning technologies such as virtual reality and immersive simulations are already known to be effective for teaching hard technical skills such as training pilots with a flight simulator. In a recent study, PriceWaterhouseCoopers set out to answer the question of whether immersive technologies can also support the development of soft skills, such as leadership, resilience, and managing through change. They selected managers from twelve US locations to take the same training on inclusive leadership in one of three learning environments: classroom, online learning environment, or virtual reality environment.
The results of the study were interesting. They showed that compared to the classroom, learners who used VR completed the task four times faster. In addition, they were 1) more confident to apply skills learned after training, 2) more emotionally connected to content than classroom learners, and 3) they were more focused on the learning task. Similar studies conducted by internal research teams at large enterprises in Finland have shown similar results.
2. Immersive Simulations Improve The Quality Of Learning Experience Which Correlates With Job Retention And Satisfaction
Immersive learning experiences such as virtual tours and immersive scenarios are not only essential for optimal results and productivity but can also have a positive impact on retention and job satisfaction. According to a survey reported by gotoHR [3], as many as 40% of employees who receive inadequate job training are at risk of leaving their job within the first year.
A recent pilot project at a transportation company in Finland tested using interactive 360-images to train bus drivers about new bus models and the related technical devices that the driver needs to operate. Employees had requested better training materials for a while, as paper manuals were hard to read and caused unnecessary misunderstandings and support requests. The results of the project were encouraging and found several benefits:
- Significant time savings
Instead of having to browse paper manuals, interactive 360-degree images of the bus cockpit were instantly available on the drivers‘ tablets. - Better communication
Short instructional videos embedded in the virtual cockpit experience made it easier for drivers with learning challenges to familiarize themselves with new bus models. - Workplace well-being
More accessible training materials taking into account drivers from different language groups were seen to improve inclusivity and overall well-being in the workplace.
3. Immersive Simulations Give Learners A Real, Safe Environment To Practice New Skills
In every workplace, employees need to constantly learn new skills, upgrade existing capabilities, or go through various kinds of compliance training. The need for in-context training is especially critical in industries where people operate in technical environments or complex service situations. Examples of these kinds of industries include manufacturing, logistics, construction, healthcare, retail, and the service industry. Dornan et al. (2019) found that in medical education, clinical practice commonly presents new doctors with situations that they are incapable of managing safely. One challenge is that students get little time to practice in real environments and situations before they start their practice. Research [4] on the topic calls for an urgent pedagogic overhaul of practice-based education.
Example: An Immersive Escape Room Simulation For Medical Students
The medical school at the University of Central Lancashire recently piloted virtual escape rooms as a way to create realistic, time-critical emergency situations for students. The pilot was led by doctors Jones and Gillaspy, who took 360-degree images of a real training room setup to simulate a sepsis patient in critical care. The idea of the escape room was to recreate a situation where students moved through a series of tasks viewing, assessing, and interpreting medical data to answer questions presented in hotspots.
Students got access to the escape room at the same time through Microsoft Teams, using channels to communicate within each group. All the students were first given a 20-minute introduction, during which the facilitators gave more context to the patient story. After this, the students had 45 minutes to solve the escape room simulation.
As the challenge began, the facilitators of the simulation were able to see that the same pressures that students would experience in a physical training room were also present in the digital situation. In the beginning, students were confused and anxious, as they became overwhelmed with new information. After a while, communication and delegation in teams improved and they were able to find the correct information to answer the questions. The simulation of a real patient situation enabled the students to get a valuable experience of how to make decisions and work with colleagues under stress. This experience makes them better prepared to deal with a similar situation in real life.
To Sum Up
Learning management systems (LMSs) and learning experience platforms (LXPs) are looking to offer more holistic learning experiences for education and employee training. The development of immersive learning technologies with easy authoring tools can bring these platforms the change they are looking for. The use of 2D, 3D, and 360-degree imagery as the base media for visual simulations allows for exploration and learning in actual work environments without the development of costly computer-generated simulations and virtual tours.
Immersive learning technologies are found to improve learner engagement, efficiency, and experience. Informational hotspots on images and videos help create structural centers for perception, giving learners the agency to explore a learning scene at their own pace. Guiding attention and interactions in digital space, informational hotspots multiply the time spent on visual media. Compared to classroom and non-immersive eLearning environments, students learning in immersive VR environments are faster than their peers.
In addition to a more contextual experience, immersive learning environments and simulations offer new options for personalization. Audio and video recordings from instructors embedded in visual learning materials make learners feel more connected. Simulations that include non-linear scenarios adapt to learners‘ choices.
Immersive scenarios are visual reproductions of real places and situations that are familiar to the learner. Embedded questions and checkpoints provide instantaneous feedback to learners who make practical choices on how to react in a certain situation. Immersive simulations from local environments allow learners to develop new skills and knowledge in a place where they can apply them in the future. Offering learners the opportunity to experience and practice skills virtually makes it much more likely that they will engage, internalize, retain, and apply the new knowledge and skills in real environments in the future.
Quelle:
Foto: HQuality/Shutterstock.com
https://elearningindustry.com/next-phase-lmss-and-lxps-smart-virtual-tours-and-immersive-simulations

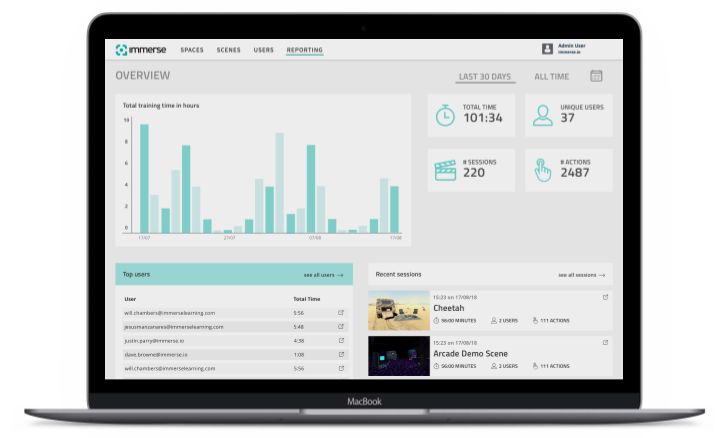 Through this simple integration, VR training can be handled in the same way as other learning content. Training can be assigned as mandatory or recommended for a job role via the learning management system (LMS). The data captured from the VR training can then be used to show competence or compliance.
Through this simple integration, VR training can be handled in the same way as other learning content. Training can be assigned as mandatory or recommended for a job role via the learning management system (LMS). The data captured from the VR training can then be used to show competence or compliance.