Cost-effective VR healthcare education in a post-coronavirus world.
As medical professionals around the globe continue to focus their undivided attention on the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, well-trained healthcare professionals are in higher demand than ever before. Unfortunately, what was already a difficult academic process has been made even more challenging due to limited resources, increased safety measures, and a multitude of other corona-induced roadblocks. This is where Innova Medical Technology comes in.
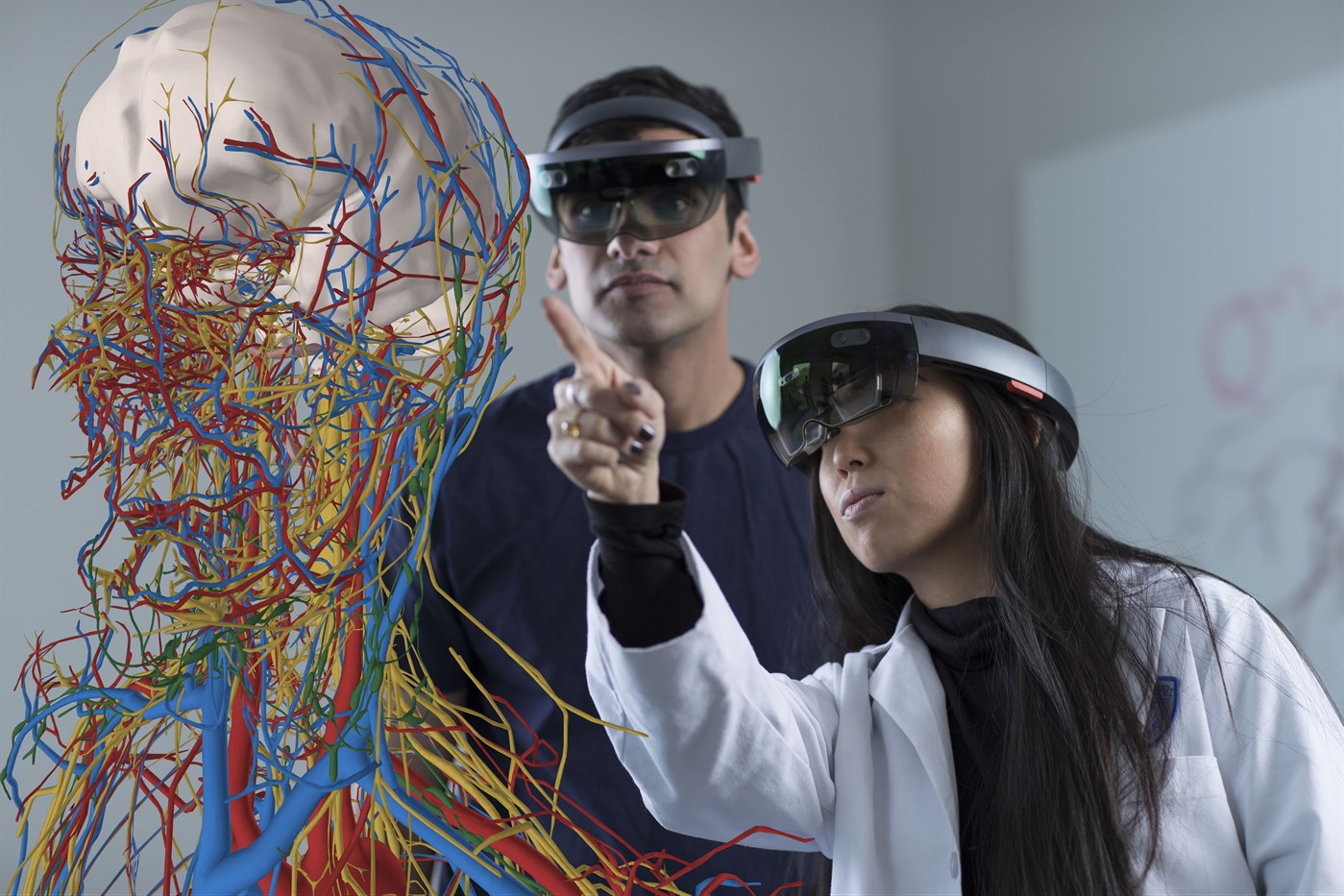
Founded by Prof. Dr. Tsai Tsuen-chiuan, a pediatrician teaching at Kaohsiung Medical University, and CEO and surgeon Dr. Chen Teh-fang, offers students a robust healthcare education platform that provides doctors-in-training with the skills and experiences necessary for clinical decision making. Referred to as V-DxM, the virtual simulation training on clinical decision making platform, is centered around highly-realistic virtual patients capable of simulating various symptoms.
This includes coughing, stomach aches, headaches, fevers, and other pains and aches. Students are then required to analyze said symptoms, consult with the virtual patient, check relevant imagery, and perform physical exams to deliver a final diagnosis. Once they’ve submitted their findings, the Innova system automatically evaluates their performance while highlighting any glaring mistakes.
“We’ve created a ‘virtual patient’ and realized our dream to revolutionize clinical education,” said Tsai in an official release. “It’s not just a product, but a complete game-changer for clinical education.”
In addition to Virtual Patients, the V-DxM platform consists of the Virtual Health Educator, interactive health education services designed specifically for patients; as well as the Flying Simulation Room, a portable medical training solution capable of replicating a professional clinical setting regardless of your location. Students can even meet up in online spaces and collaborate with one another at any given time. According to Innova, V-DxM revolves around three key technologies: efficient 3D models, medical cognition, and natural language. Since the Somatosensory Technology Park Project subsidized the company back in 2018, the platform has expanded its available use-case scenarios from 20 to 80 along with two additional modes: online remote internship and OSCE clinical examination (Objective Structured Clinical Examination, officially implemented as part of Taiwan’s National Medical Licensing Examination in 2013).
Human-centered Innovation
With hospitals around the globe in the process of cancelling internships over concerns regarding patient and doctor safety as well as available resources, Innova’s V-DxM system offers a cost-effective alternative to in-person training capable of instilling students with the knowledge, skills, and confidence necessary for clinical decision making. This technology could prove especially useful in rural areas, allowing remote students to connect with professionals and gain crucial “hands-on experience” regardless of their location and available resources.
For more information on Innova’s many educational offerings, please contact support@ennovamed.com.
KOSMOS, the XR startup Incubator Platform supported by Kaohsiung City Government, under the Somatosensory Technology Park Project, promotes creative innovation, local manufacturing and exporting total solutions. The incubator platform provides technical support, cross-industry collaboration and business consultation, making Kaohsiung a development base and hub prepping for XR startups before expanding internationally.
Quelle:
Image Credit: Innova Medical Technology
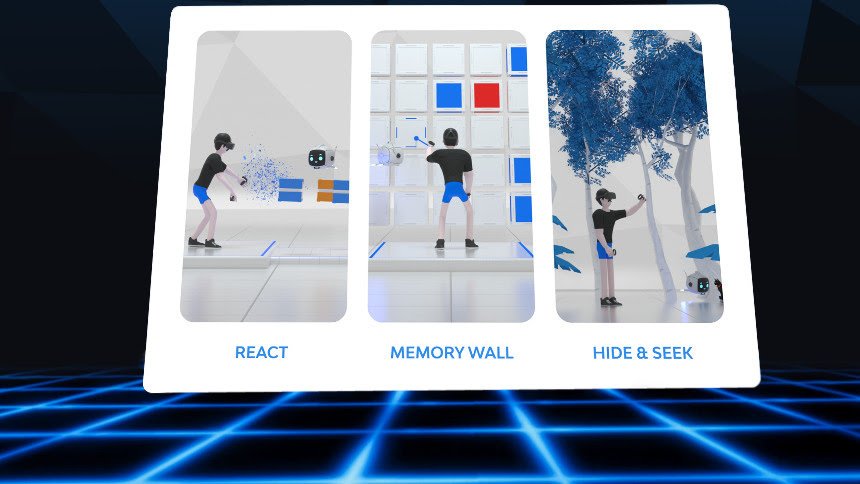

















 Virtuleap is a VR startup that is taking cognitive assessment and training to “the next level”. (Photo credit: Virtuleap)
Virtuleap is a VR startup that is taking cognitive assessment and training to “the next level”. (Photo credit: Virtuleap)